
基于热红外遥感反演的地表温度为瞬时地表温度,不同时刻获取的地表温度无法直接比较,极大地限制了其应用。通过轨道漂移纠正能够实现对瞬时地表温度的时间归一化。基于NOAA/AVHRR数据,通过NOAA企业算法反演得到瞬时地表温度,采用温度日变化模型和地表温度组分分解模型实现轨道漂移纠正,获取了青藏高原地区地方太阳时为14:30的地表温度产品(1981-2001年)。
数据下载网址:https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/56e4cbb4-bd23-42db-ab3c-6ff8a0995f83。(点击下载)
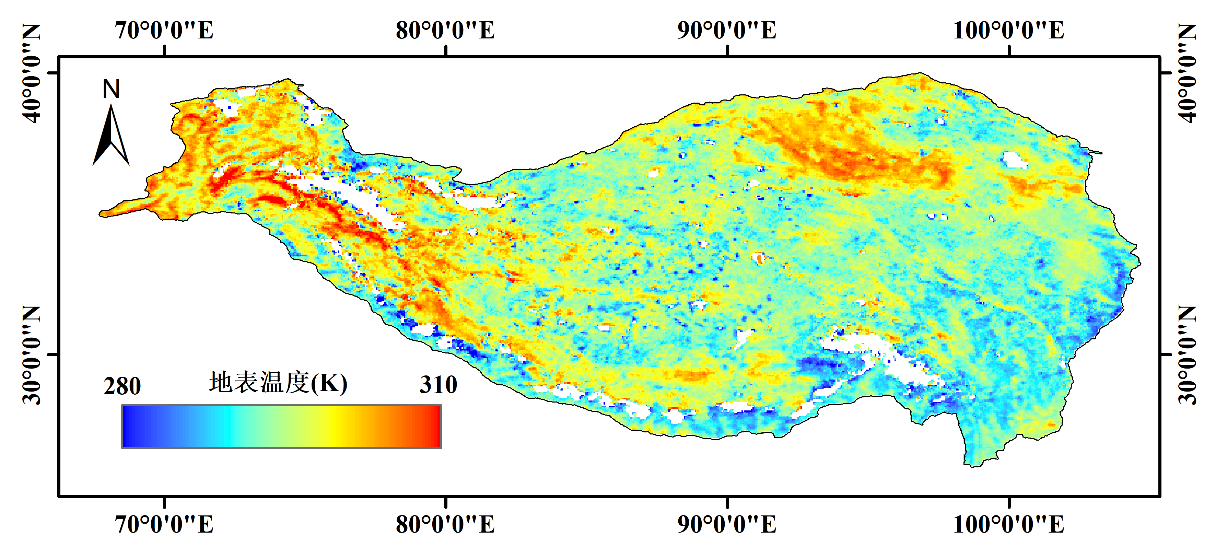
图1 1981-2001年青藏高原地区轨道漂移纠正后地表温度均值
参考文献:
X. Meng, W. Liu, J. Cheng, H. Guo, and B. Yao, "Estimating hourly Land Surface Temperature from FY-4A AGRI using an Explicitly Emissivity Dependent Split-Window Algorithm," IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, pp. 1-14, 2023, doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3285760.(点击下载)
Meng X C, Liu H and Cheng J. 2019. Evaluation and characteristic research in diurnal surface temperature cycle in China using FY-2F data. Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(4): 570–581 DOI:10.11834/jrs.20197330. (点击下载)

 所在位置:
所在位置: 



